기사본문
Bertis, early diagnosis of cancer based on blood 'proteomics+AI'
입력 2024-07-16 10:50 수정 2024-07-16 15:33
by Yoonseok Suh

▲Han Seung-man, CEO of Bertis
Bertis commercialized ‘MASTOCHECK,’ which diagnoses breast cancer using protein biomarkers in small amounts of blood, and is currently expanding its diagnostic field to pancreatic and ovarian cancers. Bertis is a company that is developing early cancer diagnosis solutions using biomarkers discovered by combining proteomics that analyze proteins, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML)-based bioinformatics technologies.
"Based on proteomics technology and AI technology, we are discovering biomarkers for early cancer diagnosis and companion diagnosis from blood, and developing diagnostic solutions using them," said Han Seung-man, CEO of Bertis. "Mastocheck, the world's first proteomics-based breast cancer diagnosis solution, has gradually increased its market share since its launch in domestic market in 2019, and is recently expanding its business to Singapore and Saudi Arabia. In the future, we will enter the United States," he said.
"Proteomics has the advantage of being able to obtain real-time information on diseases that reflect the functional traits of actually expressed proteins," he said. "The proteomics field, which is similar to the beginning of the genomics field, began with the listing of Proteomics company Seer on NASDAQ in 2020." Interest in proteomics companies is also increasing as Olink was acquired by ThermoFisher for $3.1 billion last year,
Bertis is a biotech co-founded by CEO Han Seung-man, Chief Financial Officer(CFO) Park Ji-won and Chief Marketing Officer(CMO) of Koo In-hoe in 2014. Currently, Noh Dong-young, a professor at Seoul National University College of Medicine and former president of the Korea Cancer Association, is the co-CEO, while Dr. Yoo Myung-hee is the chief scientific officer(CSO) and R&D general manager.
Bertis' core products are 'Mastocheck', a blood-based breast cancer early diagnosis solution using proteomics, and Pan-omics Analysis Service & Solution(PASS), a proteomics integrated analysis service. Mastocheck was approved by the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety in Korea in 2019 and is currently being supplied to 480 medical examination centers and hospitals nationwide. In addition to breast cancer early diagnosis products, Bertis is also researching and developing ovarian cancer early diagnosis ‘OVCHECK’ and pancreatic cancer early diagnosis ‘PANCCHECK’.
These cancer diagnosis solutions were developed based on the proteomics analysis technology established by Bertis. Bertis has ProteoID and AI-based new protein discovery technology. ProteoID is a platform technology that builds data through mass spectrometer of as many proteins as possible, secures reproducible data, and discovers differentiated biomarkers. It explained that the rapid analysis procedure in connection with this shortened the biomarker development period by 50% and reduced cost by one-tenth compared to competitors.
In addition, it used AI models to analyze data that could not be utilized in proteomics data obtained through the protein analysis method LS/MS(Liquid Chromatography-mass Spectrometry), diagnose disease conditions, and discover new biomarkers technology, SAN. BioSpectator investigated the early cancer diagnosis solution developed based on the proteomics technology built by Bertis.
Mastocheck's Early Diagnosis of Breast Cancer Based on Three Protein Biomarkers provides "83.2% accuracy"
Bertis' Mastocheck is a solution that analyzes 600,000 proteins in the blood and diagnoses three protein biomarkers, such as carbonic anhydrase(CA1), natural cell adhesion molecule like L1 protein(CHL1), and APOC1(apolipo-protein C1), which are known to be related to breast cancer, by substituting quantitative values into their own AI algorithms.
Mastocheck can diagnose stage 0, 1 or 2 breast cancer with a small amount of blood, and in particular, it showed an accuracy of 83.2%(AUC) for stage 1 breast cancer. Sensitivity and specificity were 71.6% and 85.3%, respectively. The standard used to diagnose existing breast cancer is mammography, and its sensitivity and accuracy are 63.0% and 71.3%, respectively. However, sensitivity and accuracy fall to 59.2% and 69%, respectively, in grades 3 to 4 of dense breast, which accounts for 70-80% of Korean women.
Dense breast consists of fibro-glandular tissues such as the mammary gland where breast milk is made and the ducts that carry it, and fat tissues surrounding it. When there are many fibro-glandular tissues and few fat tissues, it is called dense breast, and when the mammary gland ratio exceeds 50% and 75%, it is called dense breast in stages 3 and 4, respectively.
"In the medical field, mammography and Mastocheck are mainly used together, and in this case, the overall sensitivity and specificity are 93.9% and 83.8%, respectively, which increases compared to the case of single use,” CEO Han said. "From 10,000 in 2021 to 100,000 tests were conducted in 485 institutions last year."
Bertis has signed an agreement with SVAX(SaudiVax), one of the leading companies in the "Saudi Vision 2030 Project," to expand its operations to the Gulf Cooperation Council(GCC) region. Bertis completed a supply contract with SVAX in October last year and plans to proceed with the launch after clinical development. The Saudi Vision 2030 project is a large-scale project announced by the Saudi Arabian government in 2016 that aims to reduce their dependence on oil, develop various economic sectors, and improve the quality of life of the people. SVAX is a leading company in vaccine and biopharmaceutical production in the Saudi Vision 2030 project.
"The need for blood-based breast cancer diagnosis is high in Saudi Arabia as the breast cancer screening rate is as low as 8% for cultural and religious reasons," CEO Han said. "In addition, we signed a supply contract with Singapore's central lab and a diagnostic test company for Mast check, and sales are increasing as we expand our business to the Southeast Asian screening market."
Bertis is developing a more improved version, Mastocheck 2 with Mastocheck’s commercialization expansion. While Mastocheck is based on plasma, domestic and foreign front-line hospitals deal with more serum than plasma, so that they judged that there is a limit to market expansion. Mastocheck2 is analyzed using serum, and nine protein biomarkers were used to improve the diagnostic accuracy of breast cancer to 91.05%(AUC 0.9105). This is an improvement over the accuracy of the existing MastoCheck of 83.2%.
First, Bertis made a library for 452 proteins that could be quantitatively analyzed among the proteins found in the blood and for 852 peptides constituting them. Bertis selected 30 candidates by comparing and analyzing blood samples from breast cancer patients (50) and healthy people (50). Bertis reduced the number of candidates from 30 to 16 for protein analysis using LS-MS/MS in more blood samples from breast cancer patients(96) and healthy people(95). Afterwards, Bertis developed Mastocheck2 using nine biomarkers whose expression changed in breast cancer patients through reproducible quantitative analysis(doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-36159-4).
Bertis used his own machine learning(ML) model to analyze the accuracy of breast cancer diagnosis using nine biomarkers. Bertis trained the ML model using a total of 402 samples, including 187 healthy people and 215 breast cancer patients. The accuracy of these ML models exceeded 0.88, showing higher accuracy than the previously used molecular diagnostic methods using CA15-3 and cancer embryo antigens. Since then, 98 samples of cancer patients have been added to improve the ML model, and as a result, the accuracy for breast cancer has been confirmed to be 0.9105. Sensitivity and specificity were 87.9% and 80.7%, respectively.
Bertis has currently completed the confirmatory clinical trial of Mastocheck 2 and is collecting and analyzing the final data, and plans to proceed with the approval process as soon as the analysis is completed.
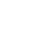
▲Process of discovering protein biomarker candidates for diagnosing ovarian cancer(HGSOC)
Early diagnosis of ovarian cancer using 18 biomarkers 'OVCHECK', "95% accuracy of predictive analysis model."
Bertis is also developing early diagnosis methods for blood-based ovarian and pancreatic cancers. According to the company, early diagnosis of ovarian cancer uses 18 biomarkers and can diagnose stage 1, 2 or 3 high-grade serous ovarian cancer(HGSOC) with 95% accuracy(AUC 0.95).
Ovarian cancer is the number one mortality rate among gynecological cancers, and most of them have no symptoms in the early stages, so 70% of patients are known to be detected after three or more stages. The survival period of ovarian cancer is known to decrease rapidly from the third stage, with a 5-year survival rate of 60-74 percent in the first to third stages, while only 41 percent, 23 percent, and 11 percent in early third, late third, and fourth stages, respectively. Ovarian cancer is a carcinoma that has hardly improved the overall survival(OS) due to treatment over the past decades, and there is a high need for a standard test for early diagnosis, Bertis explained. In particular, HGSOC targeted by Bertis is the most common type of ovarian cancer, accounting for 70% of all ovarian cancers.
Bertis conducted proteomic mass spectrometry using 26 HGSOC samples and 24 healthy human samples. Bertis identified 1847 proteins across all samples, of which 116 showed differences in expression between HGSOC patients and healthy people(doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.2c00218).
Subsequently, network modeling confirmed increased complement and coagulation cascade, IGF signaling pathway, and TGF-β signaling pathway in HGSOC samples, which selected 28 biomarker candidates. Seven of these were not found in the proteomic analysis. Of the 21 candidates, 18 exhibited statistically significant differences between samples from healthy adults and HGSOC patients(p<0.05).
Bertis confirmed the results of predictive model analysis using 18 protein biomarkers, with sensitivity and specificity of 100%, 91%, and accuracy of 95 %, respectively. In particular, the association between nine protein biomarkers and ovarian cancer was first reported through this study, Bertis explained. Bertis is currently conducting an exploratory clinical trial for OVCHECK.
Finally, Bertis developed a 'PANCCHECK' to diagnose pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma(PDAC) early with a small amount of blood. PDAC is the most common form of pancreatic cancer, and CA19-9 approved by the U. S. Food and Drug Administration(FDA) is the only blood biomarker currently for PDAC, the company explained.
Pancreatic cancer is a fatal carcinoma with a 5-year survival rate of only 12.6%, and it is located deep in the body behind the stomach, making it difficult to detect and has rapid metastasis. In general, 45% of patients diagnosed with pancreatic cancer are found with cancer spreading to other organs, and in this case, the survival rate is only 2. 4%, making early diagnosis important.
Bertis performed proteomics analysis using serum obtained from 40 patients with healthy control(HC) and pancreatic cancer(PDAC), and selected 12 protein biomarkers through various literature surveys and experiments. Since then, Bertis has analyzed the efficacy of PANCCHECK through a predictive model using samples obtained from 154 pancreatic cancer(PDAC) patients, healthy people(152), and pancreatic benign tumor patients(50).
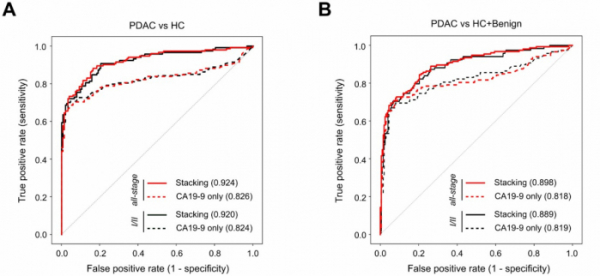
As a result of the analysis, PANCCHECK using 12 protein biomarkers and CA19-9 together showed higher accuracy(AUC) than when only CA19-9 was used for the entire stage and stage 1 and 2 pancreatic cancer (PDAC). Specifically, the analysis of PDAC patients and healthy people showed that the accuracy (AUC) of PANCCHECK was 92.4% in the entire stage, higher than 82.6% using CA19-9 alone. For the first and second phases, the accuracy (AUC) of PANCCHECK and CA19-9 were 92% and 82.4%, respectively.
Comparing PDAC patients with healthy people and those with pancreatic benign tumors, the accuracy of PANCCHECK was found to be 89.6% in the entire stage and 81.8% in CA19-9. For the first and second periods, the accuracy of the PANCCHECK was higher at 88.9% (vs 81.9%).
Bertis is currently completing PANCCHECK’s exploratory clinical trial and preparing to publish the paper of the results, and is conducting a confirmatory clinical trial for PANCCHECK s authorization.
▲Accuracy of PANCCHECK
Mass spectrometry-based Pan-omics analysis service 'PASS'.."From protein analysis to finding new drug candidates"
In addition, Bertis has developed and provided Pan-omics Analysis Service & Solution(PASS) services. Based on Bertis' ProteoID, PASS service supports the entire process from protein analysis to companion diagnosis and drug target discovery. ProteoID is a platform technology that builds data through mass spectrometer of proteins, secures reproducible data, and discovers differentiated biomarkers.
Bertis consists of five types: ‘INTEGRATED PROTEOMICS’ for qualitative and quantitative analysis of entire proteins, ‘TARGETED PROTEOMICS’ which provides quantitative analysis of target proteins, ‘SINGLE CELL PROTEOMICS’ which analyzes proteins qualitatively and quantitatively in single cells,’LIPIDOMICS’ which analyzes lipids, and ‘BIOINFORMATICS’ which provides bioinformatics-based protein data analysis and interpretation.
INTEGRATED PROTEOMICS analyzes various specimens to provide protein information related to specific diseases or conditions. It can be used for discovery of biomarkers, discovery of new drug candidates, post-translation modification (PTM) analysis, and quality control (QC) such as exosomes and target proteases(TPD).
TARGETED PROTEOMICS is a technology that can analyze less than 100 target proteins simultaneously in one sample and can be applied to protein drug quality control and measure the absolute amount of protein in a sample. SINGLE CELL PROTEOMICS uses a high-sensitivity mass spectrometer to analyze protein identification, quantitative information, and expression level differences when there is only one cell to be analyzed or only a trace amount.
LIPIDOMICS is a service that analyzes lipids composed of 4,000 different compounds and can be applied to various metabolic disease studies through lipid analysis existing inside various tissues and cells in the body. In particular, Bertis suggested that it is possible to analyze the profiling of exosome lipid composition according to the guidelines of the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety. BIOINFORMATICS is a service that provides a scientific basis for predicting mechanisms by finding diagnosis and treatment methods through bioinformatics analysis or applying them to various life phenomena.
Through this, Bertis is providing customized analysis services for developing new modality drugs such as exosomes and TPD as well as basic research. Since launching the PASS service in May 2022, Bertis has carried out 59 projects for 38 customers by the end of 2023.
관련기사
- Lunit Completes Acquisition of Volpara, Expanding into the US Market
- JD Bio, ‘HTR2A inhibitor’ MASH preclinical results “presented at the NASH-TAG...
- BnH Research's AD Treatment Strategy for cerebral cortical 'Nervous Plasticity↑'
- ImmunAbs, developing a novel C5 antibody for complement-associated autoimmunity
- DewCell Biotherapeutics, 'Three Points' to Develop Platelets that are in 'Sup...