기사본문
Immunobiome: What Is the Strategy for ‘Microbiome-based Anticancer Drug?
입력 2021-01-12 10:26 수정 2021-01-12 10:27
by Dongyoung Park
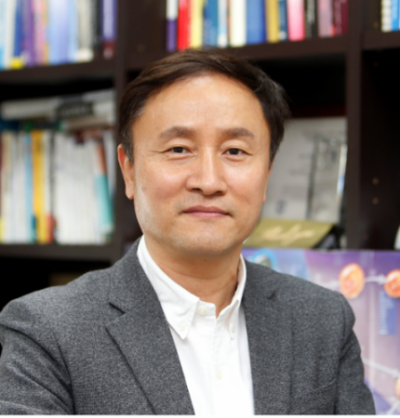

The defining quality which differentiates Immunobiome so greatly from other companies would be its specially-designed platform, which is capable of excavating not only microorganisms which manifest therapeutic effects, but also the effector molecules themselves. Representative Im Shin-Hyeog believes that it finds microorganisms which play a key role in disease, finds numerous candidates for effective substances, and clearly presents the mechanism of action.
Immunobiome has challenged the development of microbiome-based anti-cancer drug agents. As the company’s name suggests, Immunobiome intends to treat diseases through the regulation of the body’s immunity through microbiome exploitation. Evelo Bioscience and 4D Pharma, the leading companies in overseas microbiome anti-cancer drug development, have shown poor performance in PD-1 antibody-combined medication clinical trials for cancer patients. Based on a differentiable platform, Immunobiome aims to increase the chances of clinical success through the selection of treatments that can produce optimal synergy among candidates of immune checkpoint inhibitors such as PD-1, PD-L1, and CTLA-4 antibodies, based on supporting evidence.
In November, Immunobiome signed a contract with BIOSE, a French-based company specializing in microbiome CDMO(Contract Development and Manufacturing Organization), for the production of ‘IMB-001,’ the company’s lead program for anti-cancer agent development, with the development of ‘IMB-001’ beginning on the first day of last month. President Im stated, "We will start the first phase of clinical trials of IMB-001 in the fourth quarter of next year, and another anti-inflammatory lead program 'IMB-002' will enter the first phase of clinical trials in 2022. Following this schedule, we also intend to promote the IPO in 2023.”
Development of a Platform Capable of Excavating Effector Molecules of Microorganisms and Microorganisms Furnished with Therapeutic Efficacies Based on the Humanized Mouse Model
Most microbiome companies explain the working mechanisms of microorganisms which show therapeutic effects for cancer and other metabolic diseases through their excavation. On the other hand, Imunobiome has developed a platform capable of finding effector molecules of corresponding microorganisms.
Microbiome effector molecules can be classified into diverse groups of microorganism-produced metabolites, including polysaccharides on cell surfaces, exosomes, and so on. Above all, the candidate microorganisms are fractionated in order to determine the effector molecule group by which specific immunological inhibition-inducing segments or immuno-activities can be screened. As a result, if the polysaccharide segment on cell surfaces can be identified as efficacious materials, then the segment is fractionated once again, based on respective molecular weights or charges, in order to identify its structure and function.
Another advantage of the Immunobiome platform, is the use of the humanized mouse model as a preclinical model. The composition of human and mouse intestinal microorganisms hold a great deal of differences, meaning that positive results from pre-clinical trials which employ ordinary mice may exhibit a lower rate of success in actual clinics with human patients. In order to overcome these issues, Immunobiome exploits the ‘isolator,’ the experimental infrastructure for ‘germ-free’ mice, with this isolation representing an important additional step for studies concerning the microbiome. Microbiomes, originating from humans, are grafted onto germ-free mice in order to create an experimental mouse model which holds intestinal microorganisms that are similar to that of humans, thereby resulting in the best chance of attaining findings of higher clinical relevance.
IMB-001 Targeting Cancer and Inflammatory Intestinal Diseases, IMB-002 Targeting Lupus
The ‘Lead Program’ of Immunobiome consists of the ‘IMB-001,’ the therapeutic candidate material which fights against cancer, and ‘IMB-002,’ the anti-inflammatory therapeutic candidate material which is based on microorganisms that inhibit inflammatory reactions. In the case of ‘IMB-001,’ which currently exhibits the fastest speed of development, the dedicated Phase I Clinical Trial is scheduled to begin in the first quarter next year. According to President Im’s explanations, ‘IMB-001’ focuses on the apoptosis of cancer cells through T-cells that are activated through the signaling transduction of specific macrophage TLRs (Toll-like Receptors). Manifestation of polysaccharides’ activity on the surface of specific cells of ‘IMB-001’ was identified, and the active substance exhibited an anti-tumor effect at a higher or similar level to that of microorganisms in a diverse range of in-vivo mouse models which were suffering from breast cancer, colon cancer, and kidney cancer, and other diseases. In addition, Immunobiome identified the synergistic effect of the PD-L1 antibody with ‘IMB-001,’ with the paper on these results being published in the first half next year.
Another ‘lead program’ is the ‘IMB-002,’ which is the therapeutic candidate material of single-strain targeting inflammatory bowel diseases and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), with this program heading for its Phase I Clinical Trial in the 1st quarter of next year. Immunobiome published its research on the inhibition of inflammatory diseases through the use of polysaccharides on microorganisms’ cell surfaces with ‘IMB-002’, resulting in the promotion of Foxp3+regulator T cell creation, in the Journal of Science Immunology (DOI: 10.1126/sciimmunol.aat6975).
Upon the administration of ‘IMB-002’ to the mouse models which were suffering from inflammatory disease, the inflammatory disease-suffering mouse models’ weight loss was more greatly inhibited compared to that of those in the control group. Regarding its mechanism, ‘IMB-002’ inhibited the creation of IFN-γ and the proliferation of IFN-γ+ CD4+ T cells, alone with bowel length decreases which come about as a result of intestinal inflammatory reactions.
The manifestation of the identical effects from polysaccharides which reside on the cell surfaces of ‘IMB-002’ was also identified. The mouse models which were suffering from inflammatory intestinal disease were treated with the ‘Cell Surface β-glucan/galactan’ of ‘IMB-002,’ where results revealed that weight loss was more greatly inhibited, when comparing to that of the models in the control group, in addition to the treatment leading to the prevention of bowel length decreases. The polysaccharides on the cell surfaces of ‘IMB-002’ promoted the proliferation of Foxp3+regulator T cells, while also inhibiting the proliferation of IFN-γ+ CD4+ T cells.
Additionally, Immunobiome plans to expand its pipelines through the excavation of candidate materials which target the treatment of autism, multiple sclerosis, and diabetes mellitus, and other various diseases.