기사본문
G2GBIO “Fills the Gap” between “Technological Barrier and Market Needs” for Sustained-Release Preparations
입력 2021-03-08 16:41 수정 2021-03-08 16:41
by Yoonseok Suh

To date, more than 10 SRDs have been approved by FDA, USA. Among them, ‘Sandostatin LAR’, a therapeutic for acromegaly of Novartis, and ‘Invega Sustenna’, a therapeutic for schizophrenia of Janssen, are representative ones.
In fact, the patent of Sandostatin LAR by Novartis was expired in 2017. Its generics are unavailable in the market yet. Global pharmaceutical companies, such as Teva Pharmaceuticals and Sun Pharmaceutical Industries etc., have participated in the development of Sandostatin competitively. However, an application for IND to FDA is yet to be submitted. What are reasons behind such sluggishness? Making SRD seems easy, but there is a high technological barrier. President Lee Hee-yong of G2GBio stated, “… for cases of ordinary drugs with the expiry of pertinent patent rights, prices of SRD generally drop in a month or a year with the appearance of generics… however, drugs based on microsphere are typically protected by high barriers to entry of competitors…”
President Lee Hee-yong explained, “… making a small amount of a drug at a lab scale is rather easy. However, mass production of a drug following derivation of candidate formulation manifesting sustainable and constant efficacy has technological difficulty…”, “… it is usual that global pharmaceutical companies in Europe and America frequently faces failures in regulating drug release, in disabling intended pharmacokinetic reactions, and in developing process for mass production, resulting in termination of product development…”
Nonetheless, demands for drugs in the market grows further owing to the convenience of taking a drug as a medication. According to Evaluatepharma, a market research institution, the size of the market of Invega, the therapeutic with sustained-release for curing schizophrenia of Janssen, has grown from 430 million USD in 2009 to 31 billion USD in 2018. Simultaneously with a decrease of oral formulations that occupied 92% of the market in 2009 to 7% in 2018, the occupancy of a monthly injection formulation of the drug has increased to 78% from 8%. The comprehensive occupancy of sustained releasing injection formulation could reach 93% by adding the occupancy of a three-month injection formulation.
Thus, G2GBio targets to fill the gap between growing demands in market and high technological barrier in developing sustained-release drugs. Founded in 2017, G2GBio is comprised of the following human resources: President Lee Hee-yong who is responsible for the R&D in Peptron and Seol Eun-young, the Head of Research Laboratory who is responsible for the R&D of sustained-release injections in Peptron, DongKook Pharmaceutical, and Daewoong Pharmaceutical, etc. They are all experts equipped with more than 20 years of experiences pertinent to the development, technology transfer, and commercialization of sustained release drugs. Further, G2GBio has invited Dr. Raymond Bartus from Alkermes, who has developed and released diverse kinds of SRDs, and Dr. Mark Tracy as members of the SAB.
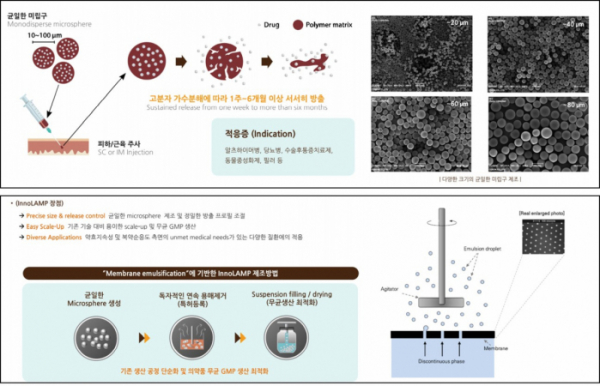
G2GBio is developing incrementally modified drugs (IMDs) of efficacies sustainable from weeks to a month via single administration, which are applicable to dementia, diabetes mellitus, post-operative nonopioid analgesics, etc. Existing drugs of proven efficacies are employed for the fabrication of uniform microspherical structures by using biodegradable polymers. According to the size and composition of biodegradable polymers fabricated, the duration of each drug to be released in bodies could be regulated.
President Lee Hee-yong stated, “… to date, there are only 10 or more SRDs presently approved by FDA in USA...”, “… based on experiences of successful commercialization of products from R&Ds, we will develop SRDs in microspheres using biodegradable polymers for patients who have difficulties in administering drugs for a long time or uptaking drugs ...” For SRDs based on microspheres, the biggest difficulty resides in the mass production of SRDs with uniform quality. He stated that G2gBio has secured technologies pertinent to mass production with higher level of yield rate, uniform quality, and reproducibility of SRDs. President Lee Hee-yong stated, “… based on the manufacturing process developed spontaneously, we have secured the manufacturing process for mass production in a rather short period of time, as well as the process capable of filling drugs in a completely aseptic condition…”
Biospectator summarized the technologies for producing SRDs and current state of drug development pipelines of G2GBio as follows.
▲InnoLAMP platform
◆ The ‘InnoLAMP’ technology grasps Quality, Yield, and Time of Fabrication of SRDs
The key technology of G2GBio, the innovative long acting microparticle (InnoLAMP), enables the fabrication of microspheres of drug substance mixed with biodegradable polymers. Depending on the ratio of the substance constituting biodegradable polymers, the speed of drug substance of microsphere to be released into body is controlled to sustain the efficacy of the drug from weeks to more than 6 months. For the case of SRDs in microsphere, processes of fabrication thereof can be distinguished into the following: ① Fabrication of Uniform Microspheres, ② Removal of Solvents, and ③ Aseptic Condition.
G2GBio differentiated its process in that it realized breakthrough of limitations in the manufacturing process of SRDs employing existing microspherical structures in a way of their own. Above all, G2GBio prepared the equipment for punching holes of uniform size on a stainless plate. By passing the mixture of substance of SRD with biodegradable polymers through these holes, they were able to secure the technology capable of producing microspheres with uniform quality, thereby improving the productivity and shortening the process of manufacturing.
President Lee Hee-yong stated, “… we have introduced a membrane equipment and concluded an exclusive contract with Micropore Technologies in the United Kingdom…”, ”… the proprietary technology enabled us to prompt mass production of SRDs with a high yield rate of microspheres to the amount of few kilograms per hour…”
Conventional methods of producing SRDs undergo an emulsifying process of drug substance and polymers, followed by the removal of solvents, recovery, drying, crushing, and filling processes. The manufacture of emulsion has to exploit high-speed agitation technology by employing existing approach, resulting in inhomogeneity of microspherical particles requiring filtering and recovery processes. Furthermore, the process of removing solvents rendered the production of SRDs. Manifesting constant pharmacokinetic properties becomes difficult to degrade the productivity. In addition, it inhibits the following processes: drying, crushing, and filling in vials under aseptic conditions for preparation of injections. Contrarily, G2GBio differentiated its manufacturing process. It is capable of exploiting lyophilization of microspheres of mass production that enables filling in vials under an aseptic condition conveniently by using the InnoLAMP technology.
◆ Phase I Clinical Trial of ‘Donepezil’, a Type of Monthly Sustainment, is Scheduled to be Completed This Year
G2GBio primarily targets the market of therapeutics for dementia which requires daily administration of drugs. For dementia in patients of old age who are being affected dominantly, they might have difficulties in taking pertinent drugs daily. G2GBio targets the development of an injection-sustainable, the ‘Donepezil’, for a month, aiming for improving patient compliance of medication. By using ‘Donepezil’, the company intends to avoid the occurrence of adverse effects of existing oral or patches appearing in GI tract or skin reactions. Currently, G2GBio is developing a monthly injection of a candidate therapeutic for dementia, the ‘GB-5001(Donepezil)’. It is preparing for a Phase I Clinical Trial in Canada scheduled to be completed within this year.
President Lee Hee-yong stated, “…we will promote the technology transfer upon completion of the Phase I Clinical Trial…”, “… due to recognized efficacy of ‘Donepezil’, progression to a Phase I Clinical Trial is approved to determine its safety and appropriate dosage.” He continued, “… For the clinical trial, the facilities of manufacturing for clinical trial and commercialization need to be identical to each other, thus, we will employ facilities of global CMO companies…”
Another candidate material of therapeutics for dementia is ‘GB-5112’, a type of sustainable-release of ‘Rivastigmine’. Rivastigmine works by inhibiting both AChE and BuChE, different from Donepezil, which is an inhibitor of only AChE. Rivastigmine is known to exhibit therapeutic effects on 54.5% of patients who have failed to get favorable results from Donepezil and on 74.4% of patients who have terminated treatment with Donepezil due to its adverse effects. Rivastigmine is also known to have beneficial effects by improving nervous and mental disorders of patients suffering from dementia such as of insomnia, deteriorated appetite, anxiety, and so on. Currently, G2GBio is optimizing the formulation and focusing on the scale-up of pertinent process at its preclinical stage.