기사본문
Genome Opinion, "Developing NGS-based mutation Analysis Method for Liquid biopsy Solution"
입력 2018-11-08 09:59 수정 2018-11-08 17:51
by Euna Lee
Established October 2017, challenging the field of liquid biopsy method utilizing machine learning and genomics. Extensive NGS Analysis know-how, focusing on “ctDNA detection and a New potential Biomarker ‘Clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP)’ research’...” “Exploring utilization in the diagnosis and monitoring of solid cancer, blood cancer, and cardiovascular disease”.
Genome Opinion is a company specializing in clinical application of next-generation sequencing (NGS)-based genome analysis and liquid biopsy using Omics data analysis techniques, such as protein and RNA.
Choonghyun Sun, CEO of the Genome Opinion, recently met Biospectator, and said, “ultimately, our goal is to develop an early diagnosis and monitoring tools for lung cancer, colorectal cancer, blood cancer, and cardiovascular disease, combining the NGS technique, circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) test, and new biomarker, the clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP). In particular, we are developing an artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm to eliminate false positive signal from ctDNA NGS data .”

▲사진에서 왼쪽부터 지놈오피니언 공동창업자인 송한 이사, 선충현 대표이사, 임호균 이사
◇ New Potential Biomarker, ‘Clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP)’
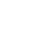
Genome Opinion detects circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) with a NGS-based liquid biopsy biomarker. In addition, the Genome Opinion focuses on a new potential biomarker, clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP). CHIP refers to hematopoietic stem cells that have mutation in normal hematopoietic stem cells, due to factors such as aging, chemotherapy, and environmental stress. The significance of CHIP has begun to emerge with the accumulation of whole-exome sequencing data over the past decade. CHIP is simply a pre-cancer cell. That is to say, CHIP has high potential of becoming full-blown leukemia. For this reason, the detection of CHIP in early cancer diagnosis can be beneficial. Research shows a link between presence of CHIP and increase in primary and secondary hematological cancer risk.
▲클론성 조혈증(Clonal Hematopoiesis of Indeterminate Potential, CHIP) 개념 설명 (그림: 지놈오피니언 제공)
“A mutation that causes blood cancer has been identified in CHIP and CHIP-carriers show increase in blood cancer risk for more than 10 times, and increase in secondary blood cancer risk of 4 times. Although prospective studies are still needed, this means that CHIP can be used as a potential marker for screening patients at risk of the development of myeloid neoplasm”, Sun explained.
More surprisingly, CHIP increases the risk of death related to cardiovascular disease. Study shows CHIP increases the risk of cardiovascular disease by (2 to 4) times, including coronary heart disease and myocardial infarction.
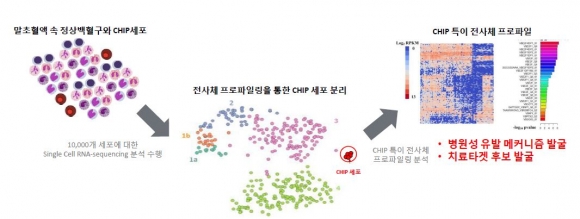
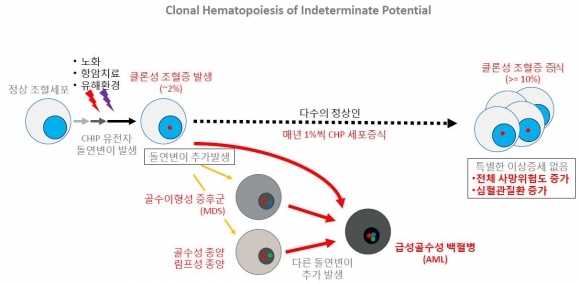
▲클론성조혈증(CHIP)의 치료타깃 마커 발굴 플랫폼 (그림: 지놈오피니언 제공)
Genome Opinion is also using CHIP to develop therapeutic targets for novel drugs. The plan is to establish a biomarker discovery platform through utilizing single-cell RNA sequencing technology . Currently, Genome Opinion is developing a kit for health screening that predicts the risk of cardiovascular disease using CHIP. They expect it to be launched next year.
He added, “Another reason to pay attention to CHIP is to increase the accuracy of ctDNA detection on NGS base. Until now, CHIP was contributing to false signal in the mutation analysis step that we missed, because we were unaware of these cells.. But now, we can distinguish cancer cells from CHIP-derived DNA to detect false positives.”
◇ NGS-based ctDNA, three key analytical technologies
Genome Opinion optimizes detection accuracy starting from selection of reagent and at the level of data analysis when analyzing ctDNA data based on NGS. In particular, they have know-how to eliminate false positives, such as filtering based on noise data derived from peripheral blood cells.
“We use machine learning to differentiate real from noise sequencing signal in abnormal blood cells. The point is that this technique utilizes a database of Korean specific nucleotide sequence variations”, CEO Sun said.
In particular, the Genome Opinion distinguishes CHIP-derived DNA to reduce the noise in ctDNA detection. He emphasized, “In this year’s ASCO, a genetic mutation derived from CHIP at the time of liquid biopsy shown to increase false positives. We should distinguish CHIP-derived mutations and cancer-derived mutations in ctDNA data analysis stage.”
Second method employs noise variation filtering using a molecular barcode. “We have technically complemented both sequence clustering techniques for molecular barcode processing and data analysis, DNA library reagents using molecular barcodes, and target enrichment reagents. We reduced the false-positive sequence variation by three times and improved the accuracy compared to the existing method”, Sun explained.
Lastly, we implement a process that eliminates the false positives by using the test-specific error database. We establish a database and a statistical model for eliminating false mutations in such as oxoG, due to the oxidation caused by DNA sonication. We can also detect a fusion gene. and copy number variation (CNV) and indels.
Currently, Genome Opinion is developing NGS analysis pipeline using clinical and genetic data. One clinical cohort study will be looking at a cardiovascular disease risk comparing an existing monitoring model and one that combines CHIP information with existing tests. They hope to develop this as a health screening product. They expect clinical results to be secured next year. Also, In Vitro Diagnostics (IVD) for the diagnosis of lymphoma and myeloma through ctDNA testing is under development. In the future, the target will be expanded to lung cancer and colorectal cancer indications, and liquid biopsy-based diagnostic kits will be developed for various diseases.